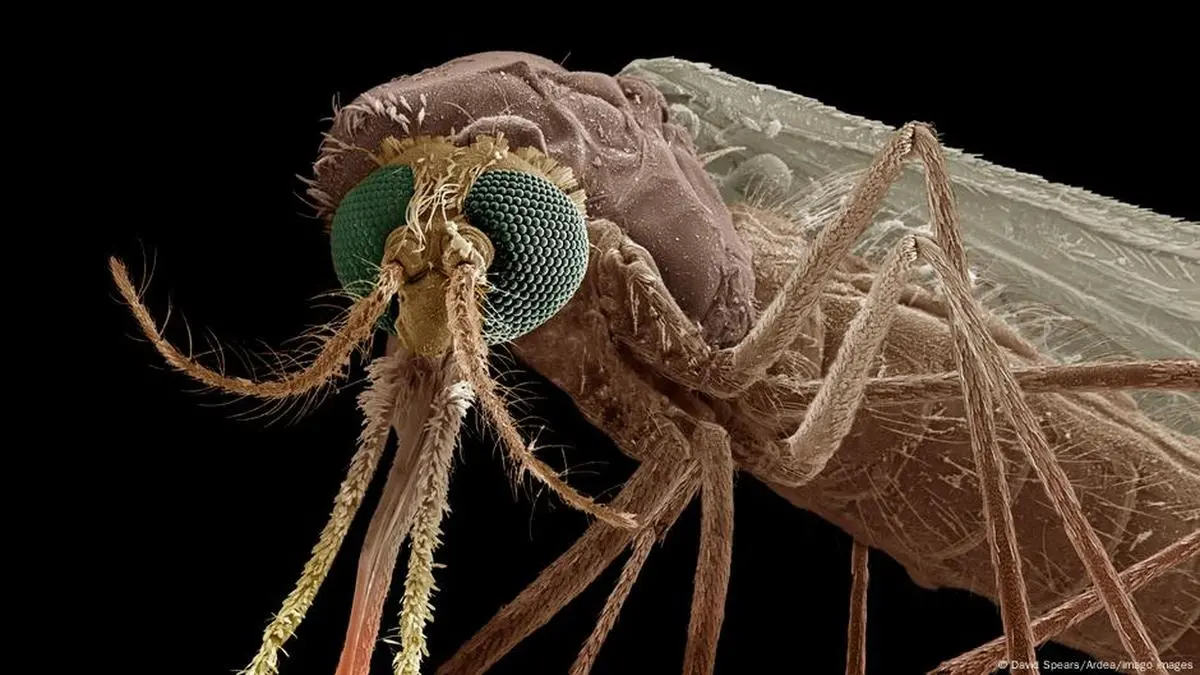
A drug used to deal with a uncommon inherited illness has been discovered to make human blood poisonous to malaria-carrying mosquitoes. It may present one other instrument to scale back lethal insect populations.
Mosquitoes are thought of the deadliest animal on the planet—carrying ailments that kill multiple million individuals a yr. Scientists have discovered {that a} drug known as nitisinone, which is used to deal with individuals with a uncommon inherited illness known as tyrosinemia, makes human blood poisonous to mosquitoes.
Though it doesn’t forestall the transmission of the malaria parasite Plasmodium, nitisinone is now being thought of for additional area exams as a chemical management to scale back the variety of bugs able to spreading the illness.
What’s the mosquito-killing drug?
Nitisinone is used to deal with hereditary tyrosinemia kind 1, which is a illness the place individuals have an excessive amount of tyrosine of their blood.
Additionally Learn | Is India falling wanting its deadline of eradicating malaria by 2030?
Lab exams discovered that when a mosquito bites somebody who has been taking nitisinone, the presence of the drug prevents the insect from with the ability to digest the human “blood meal” — 24 hours later, the insect dies. Nitisinone is poisonous to mosquitoes in a manner that it’s not to people.
In contrast with ivermectin, one other chemical that has been investigated as a mosquito vector management, nitisinone lasts longer within the bloodstream. It is usually versatile, as it may be vaporised and sprayed on surfaces, that means it could act like an insecticide.
An insecticide in your blood?
Whereas area exams are required to make sure the drug is efficient in malaria-prone areas, the early findings counsel it might be promising as an inexpensive and efficient agent to manage mosquito numbers. Importantly, it seems efficient towards mosquito species which have developed resistance to different management chemical substances.
“It kills insecticide-resistant mosquitoes. There are a number of pesticides which have been used within the area for many years [but] there are resistant [mosquito] traces locally,” stated Alvaro Acosta-Serrano, the joint supervisor of the examine, based mostly at Notre Dame College, US. “We examined these resistant traces with nitisinone and they’re virtually as equally vulnerable because the vulnerable traces of mosquitoes. It brings lots of advantages, not solely to say that it performs higher than ivermectin.”
“Current reviews have urged the Trump administration could reduce funding for well being initiatives like malaria as a part of a broader culling of applications supported by USAID.”
Anna Final, an affiliate professor in infectious ailments on the London Faculty of Hygiene and Tropical Drugs, who was not concerned within the examine, stated the findings had been promising, notably given outcomes from latest area exams of ivermectin in weak communities in Africa. “It’s a really related piece of labor, I feel, and does observe on from the marginally disappointing outcomes from nearly all of area trials taking a look at ivermectin, which confirmed that it didn’t carry out in the best way that we had anticipated and hoped, within the area,” Final informed DW.
What strategies are there to scale back mosquito-borne ailments?
The newest World Well being Group information estimated that 263 million individuals had been contaminated with the malaria parasite in 2023, leading to 597,000 deaths. However there are a number of medical and technological instruments for preventing mosquito-borne ailments like malaria.
Medical and social interventions are believed to have prevented 2.2 billion circumstances and 12.7 million deaths since 2000. The RTS,S vaccine, marketed as Mosquirix, for instance, is 30 per cent efficient at stopping extreme circumstances and requires 4 doses. Different vaccines are additionally in improvement.
Mosquito nets handled with pesticides are additionally essential instruments. They’re extensively distributed throughout communities by varied NGOs and well being our bodies.
Just like the vaccine, nets are about “30 per cent efficient”, in accordance with Estrella Lasry, a senior malaria adviser on the International Fund to combat AIDS, Tuberculosis and Malaria. “We attempt to cowl as excessive a quantity as doable of the [malaria vulnerable] populations,” Lasry stated.
However in addition to insecticide use on nets and within the surroundings, insect management stays an essential measure for teams attempting to manage the illness. This consists of larval management—killing off mosquito hatchlings earlier than they mature.
Can malaria be eradicated?
Malaria has already been eradicated from a number of nations in Latin America, Africa, and Asia. Nonetheless, there’s a danger that measures to include the virus the place it persists could stall if teams are unable to ship providers.
Additionally Learn | Antimicrobial resistance is a big risk—new deal affords hope
Current reviews have urged the Trump administration could reduce funding for well being initiatives like malaria as a part of a broader culling of applications supported by the US Company for Worldwide Growth (USAID). There are additionally considerations of wider US cuts to medical analysis at residence and overseas.
“It’s a extremely essential concern in the intervening time. I feel it will likely be devastating for well being programs and applications, actually throughout sub-Saharan Africa,” Final stated. “However it is going to seemingly be wider reaching than that, I feel, within the context of improvement of latest molecules corresponding to nitisinone. There must be lots of concentrate on sustaining and sustaining current glorious instruments that now we have which have actually made enormous good points within the final decade or extra.”