India’s city facilities are grappling with a extreme air air pollution disaster that poses a major risk to public well being and concrete livability. Studies recommend that every 12 months, Delhi data roughly 12,000 air pollution-related deaths, accounting for 11.5% of its whole fatalities.
Delhi’s air high quality disaster just isn’t a brief inconvenience, regardless of what the heavy-pollution winter months may recommend. It’s a year-round, systemic problem. Reactive measures like short-term bans and emergency interventions, although crucial in excessive conditions, don’t deal with the foundation causes of air air pollution within the metropolis.
Delhi’s Air Air pollution Problem
As per the 2018 source apportionment study for Delhi, vehicular emissions are a major driver of air air pollution, contributing near 19% particulate matter (PM) 10 and 39% PM 2.5 air pollution. The Delhi Statistical Handbook 2024 means that the full variety of registered automobiles has reached roughly 1.48 crore (14.8 million), with 54.6 lakh (5.46 million) two-wheelers and 20.8 lakh (2.08 million) personal automobiles making up greater than 50.7% fleet. Whereas town has applied notable measures, such because the compressed pure fuel (CNG) mandate for public transport, the surge in private car possession has offset these beneficial properties.
Based on the VAHAN dashboard, Delhi’s car fleet exceeds 15 million, rising by 700,000 yearly. The continued operation of over 1.3 million Bharat Stage-III automobiles additional compounds this problem. These older, high-emission automobiles, which observe the older emission requirements and are reaching their finish of life, proceed to function on account of ineffective deregistration and scrapping mechanisms. Regardless of Delhi’s efforts to curb vehicular air pollution by age restrictions, a considerable portion of its on-road fleet includes automobiles from neighboring states with much less stringent laws. This inflow of older, extra polluting automobiles exacerbates each site visitors congestion and air high quality, necessitating fast and focused interventions.
What Are Low-Emission Zones?
Establishing low-emission zones (LEZs) presents a strategic method to cut back vehicular emissions and enhance air high quality within the metropolis. LEZs, applied in over 300 cities globally, together with London, Jakarta and Berlin, prohibit or penalize high-emission automobiles, encouraging cleaner alternate options like EVs, public transport and shared mobility. These zones have been instrumental in lowering vehicle-related emissions and selling sustainable city mobility. LEZs may construct on present measures akin to no-vehicle zones, pedestrianized streets, and EV insurance policies mandating EV adoption and fleet renewals.
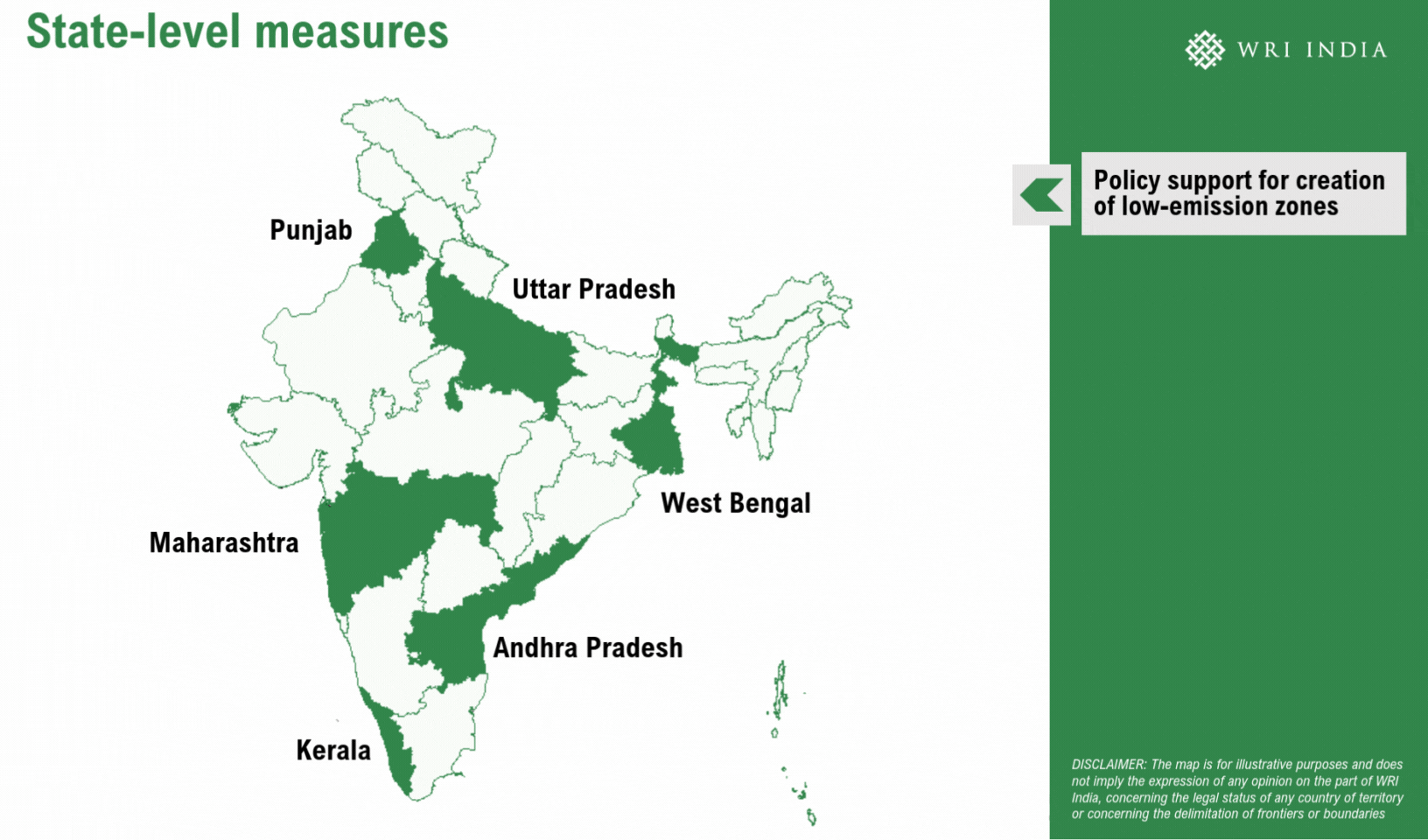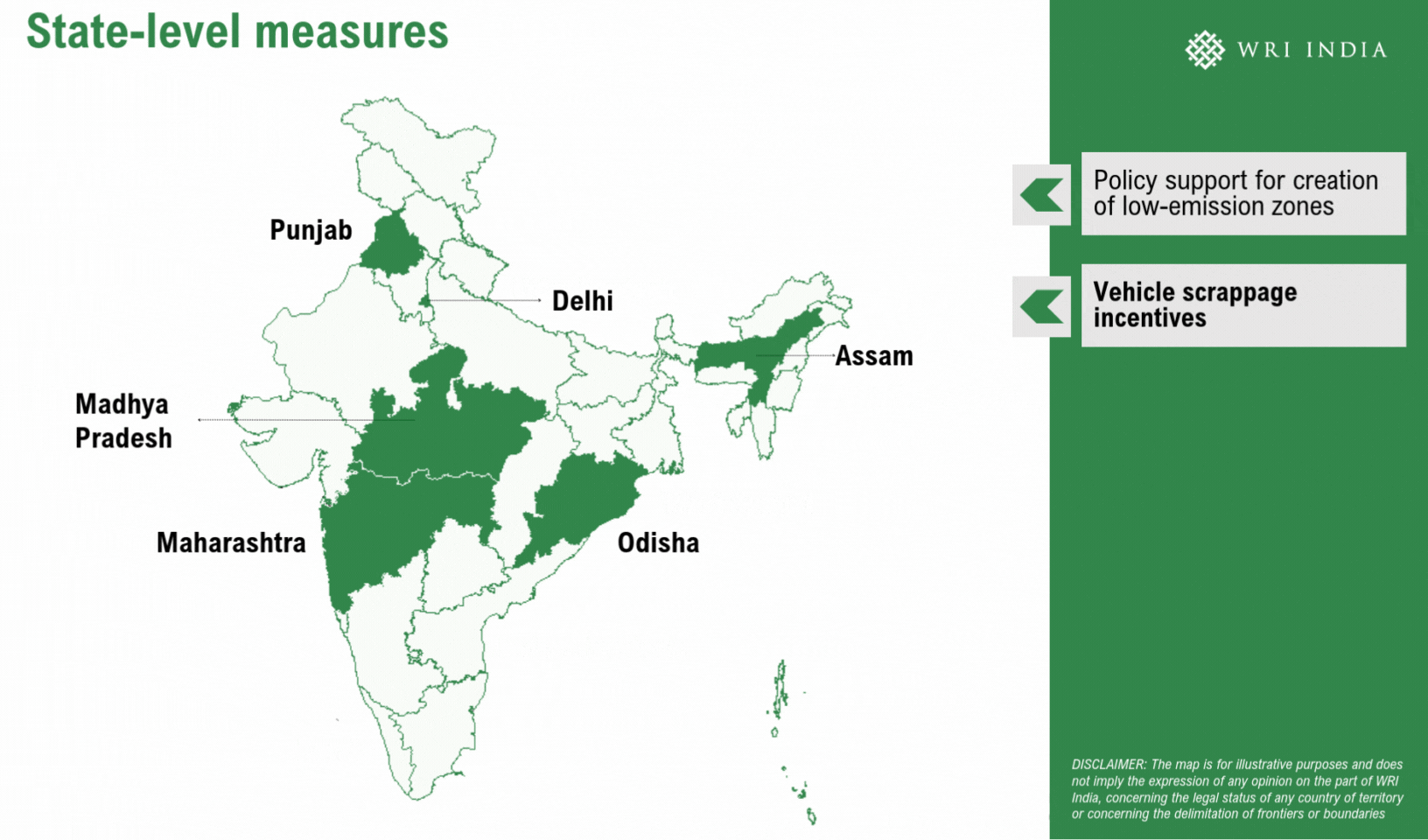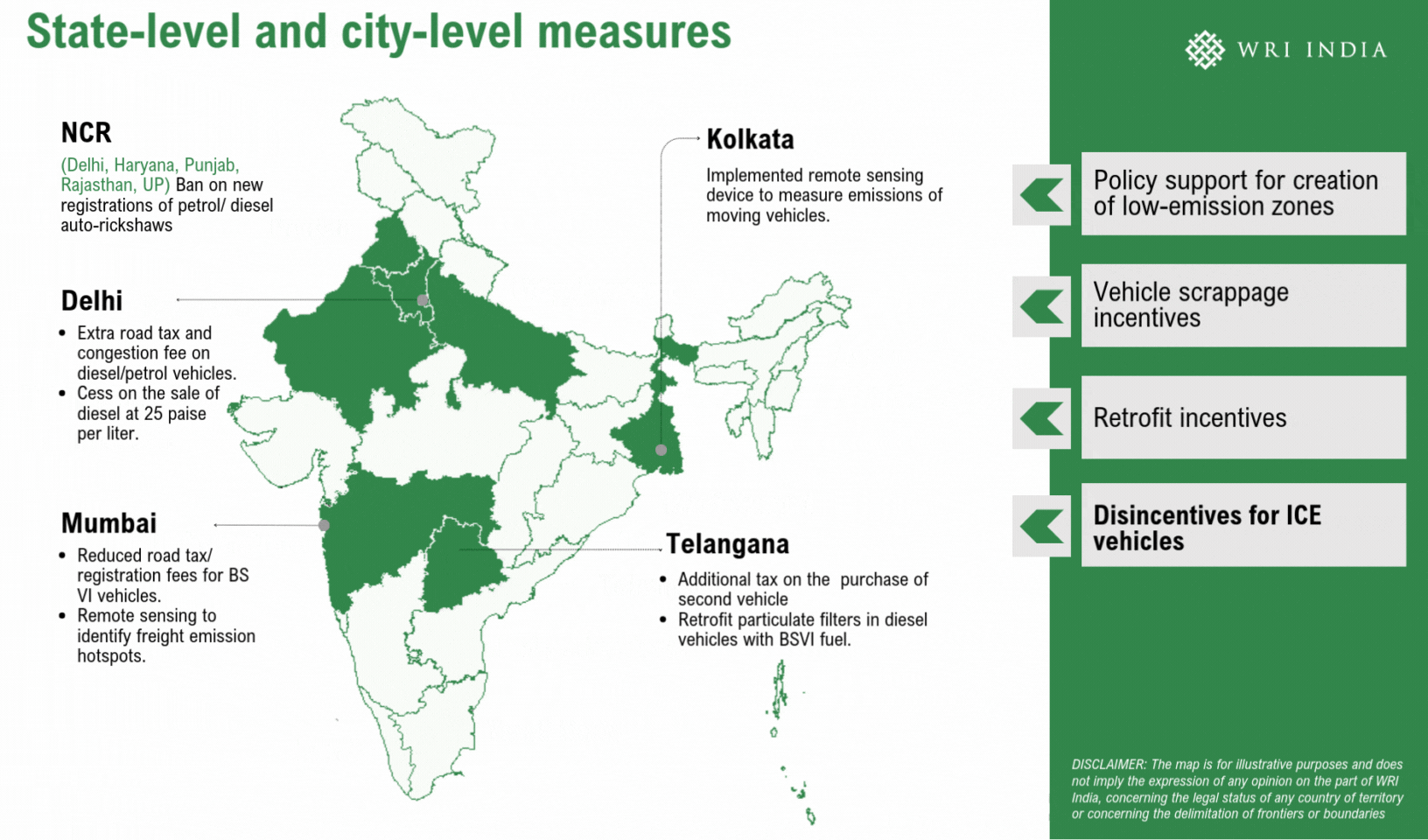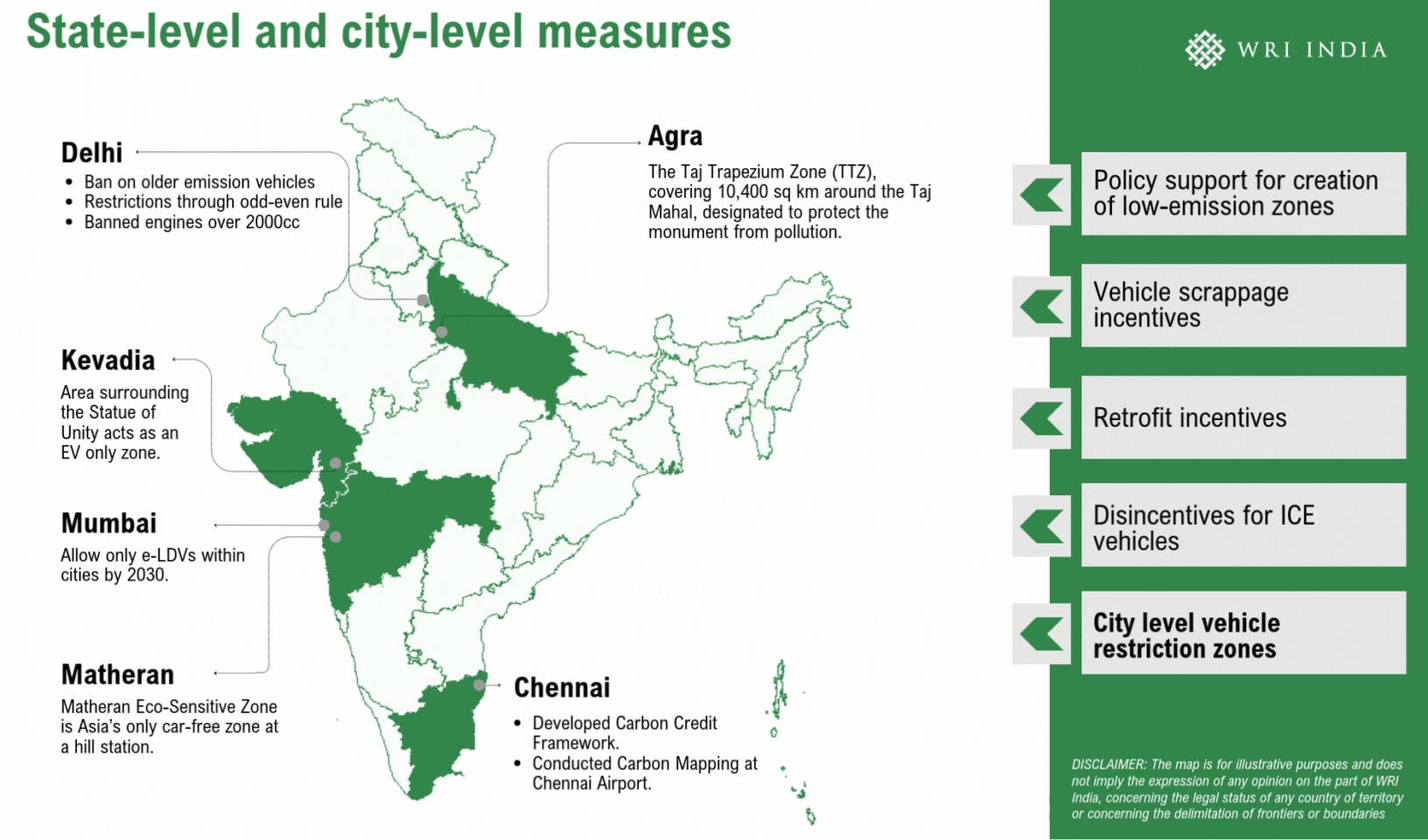
Viability of Low-Emission Zones for Delhi
Delhi can implement LEZs by a phased method over 5 years, proactively concentrating on year-round emission reductions. This can even allow swift enforcement of stringent measures throughout extreme air high quality episodes underneath the Graded Response Motion Plan (GRAP). Strengthening Automated Quantity Plate Recognition (ANPR) digicam methods can successfully prohibit extremely polluting automobiles from coming into designated areas. Furthermore, coupled with acceptable incentives, the LEZ can nudge a modal shift in direction of cleaner automobiles, as demonstrated in international instances. A number of the key alternatives for LEZs embody:
-
Attaining focused motion: Delhi’s efforts to curb vehicular air pollution by stricter requirements and public transport growth face enforcement challenges on account of excessive car volumes. Implementing LEZs in smaller, well-defined areas can improve enforcement and coordination. This additionally units the stage for broader initiatives with the potential for important regional affect.
-
Supporting present insurance policies: LEZs align intently with broader regulatory and coverage frameworks, together with national-level norms like Company Common Gasoline Effectivity (CAFE III), which inspires automakers to supply decrease CO2-emission automobiles. In addition they complement state-level initiatives such because the Delhi EV Coverage – which presents demand-side and supply-side incentives for EV adoption, the Delhi Motor Automobile Aggregator, and the Delhi Service Supplier Scheme – which mandates the transition of shared mobility companies to EV fleets.
-
Authorized feasibility: Delhi’s sturdy authorized framework additionally helps LEZ implementation. As an example, the Air (Prevention and Management of Air pollution) Act, 1981, empowers air pollution management boards to declare air air pollution management areas. Equally, the Motor Autos Act, 1988, permits regulation of vehicular motion in designated areas. The New Delhi Municipal Council (NDMC) Act, 1994, additional permits environmental initiatives, making the NDMC space appropriate for an LEZ pilot.
Implementing LEZs presents related advantages past simply cleaner air. By lowering vehicular emissions, Delhi can decrease charges of respiratory and cardiovascular illnesses, easing healthcare prices for each town and its residents. Studies recommend that cleaner air improves public well being, enhances productiveness by lowering sick days and boosts total well-being. Economically, LEZs can appeal to companies, buyers and vacationers, driving town’s progress. Prioritizing EVs and shared mobility inside these zones additionally helps international local weather targets, positioning Delhi as a pacesetter in sustainable city growth.
It is very important acknowledge the constraints of LEZs. Whereas efficient at lowering native vehicular emissions, they don’t deal with air pollution from broader airshed-level sources. Points like poor air high quality from stubble burning in neighboring states or wind-carried industrial emissions might proceed to affect the area, limiting the fast affect of LEZs on transboundary air pollution. To deal with these challenges comprehensively, LEZs must be built-in right into a broader technique that features regional collaboration and airshed-level interventions.
With present legislative frameworks, sturdy infrastructure and administrative capability, Delhi is well-positioned to efficiently implement LEZs. By embracing this proactive method, town can pave the way in which for a cleaner, more healthy and sustainable future.










