GENDER INEQUALITY IN MSMES AND CREDIT ACCESS FOR WOMEN
TOPIC: (GS3) ECONOMY: THE HINDU
Latest information reveals that regardless of a number of schemes, women-led MSMEs face a persistent credit score hole and restricted assist, highlighting deep-rooted gender inequality in India’s enterprise atmosphere.
Standing of Girls in MSMEs
- Girls’s Share in MSMEs:
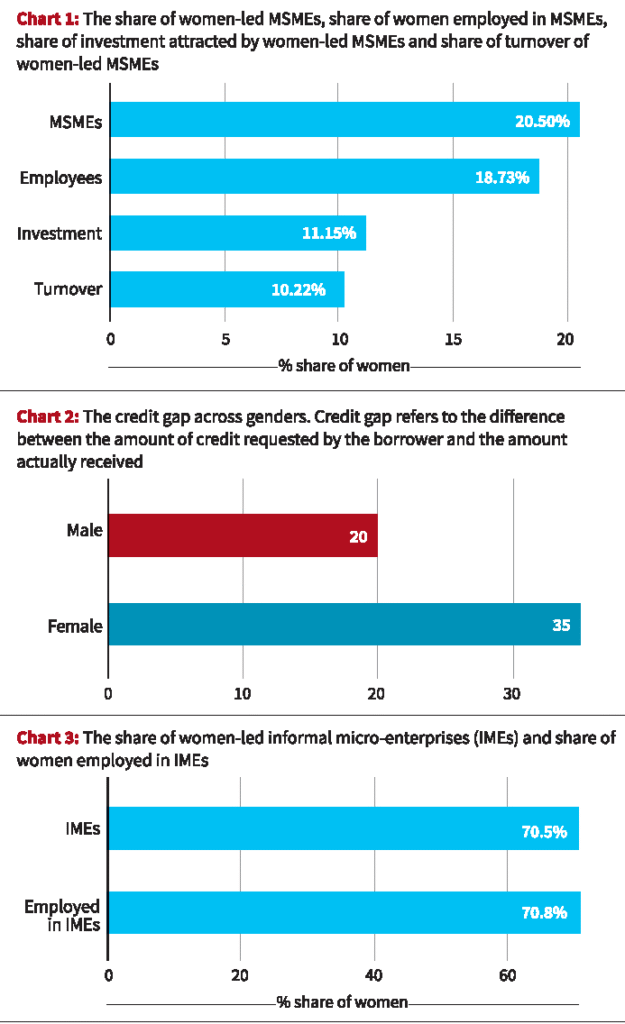
- Girls personal solely 20.5% of MSMEs in India.
- They characterize 18.73% of MSME staff.
- Solely 11.15% of complete funding goes to women-led MSMEs.
- Turnover share is simply 10.22%, exhibiting low income technology.
- Credit score Hole: Girls face a 35% credit score hole, whereas males face a 20% hole. This implies over a 3rd of their credit score wants are unmet.
- PM MUDRA Yojana (PMMY): Girls maintain 64% of mortgage accounts beneath PMMY. However they obtain solely 41% of complete mortgage quantity, exhibiting funding disparity.
Challenges for Girls Entrepreneurs
- Entry to Credit score: Girls are sometimes seen as dangerous debtors as a result of lack of collateral. Many companies are casual and thus not eligible for formal loans.
- Consciousness Hole: Many first-generation ladies entrepreneurs, particularly in rural areas, have low monetary literacy. They’re typically unaware of schemes or lack assist in utility.
- Discrimination in Banking: It takes ladies practically twice as many financial institution visits as males to get loans. Banks hesitate to lend as a result of perceived danger and absence of property possession.
- Dependence on Casual Credit score: Resulting from mortgage rejection or delays, many flip to casual sources, which cost excessive curiosity and are dangerous.
Standing of Casual Micro Enterprises (IMEs)
- Over 70.5% of IMEs are women-led, and 70.8% of IME staff are ladies.
- IMEs stay largely excluded from formal credit score, regardless of being registered on the Udyam Help Portal.
Authorities Efforts and Shortcomings
- Schemes like PMMY, Udyam Help Portal, and PLI have aimed to spice up ladies entrepreneurship.
- Implementation points, ignorance campaigns, and banking reluctance stay main limitations.
Means Ahead
- Enhance credit score entry with particular lending home windows and decreased collateral necessities.
- Broaden monetary literacy packages focusing on rural ladies.
- Practice financial institution employees to sensitively deal with mortgage purposes from ladies.
- Strengthen implementation of schemes with native hand-holding assist.
Conclusion
Regardless of the big variety of women-led accounts beneath authorities mortgage schemes, funding and credit score gaps stay vast. Bridging these divides is essential to making sure inclusive financial progress and attaining objectives beneath Atmanirbhar Bharat and SDG 5 (Gender Equality).
REMAKING THE NUCLEAR ORDER IN WEST ASIA
TOPIC: (GS2) GOVERNANCE: THE HINDU
Israel not too long ago carried out navy strikes on Iran’s nuclear amenities with U.S. assist, reshaping the stability of energy in West Asia and elevating considerations over nuclear deterrence, regional stability, and diplomacy.
Iran-Israel Nuclear Tensions
- Israel goals to stay the sole nuclear energy in West Asia.
- Iran insists on its proper to nuclear know-how beneath the Nuclear Non-Proliferation Treaty (NPT).
- The 2015 JCPOA (Iran nuclear deal) allowed restricted uranium enrichment, which Israel opposed.
- Latest Israeli strikes, supported by the U.S., focused Iranian nuclear and navy property.
Why the Battle Escalated
- Israel’s Technique: PM Netanyahu seeks to forestall even peaceable nuclear progress by Iran. The assaults adopted home stress in Israel and a weakening of Iran’s regional allies.
- Iran’s Missteps: Assumed continued U.S. restraint and underestimated Israel’s intelligence attain. Was criticized by IAEA for low cooperation and growing uranium enrichment.
- U.S. Position: Initially reluctant however joined after Israel’s preliminary success. U.S. used heavy aerial weapons to destroy suspected underground Iranian nuclear websites.
Iran’s Nuclear Journey
- Started a civilian nuclear programme within the Nineteen Fifties.
- Developed clandestine enrichment after the Iran-Iraq conflict.
- Aimed to be a “threshold nuclear state”—near weapons however not crossing the road.
- Now, as a result of rising threats, a full deterrent is being reconsidered.
Geopolitical Implications
- Iran’s proxies like Hezbollah and Hamas are weakened.
- Gulf States really feel briefly safer, however worry long-term instability.
- Talks between U.S. and Iran are unsure as a result of damaged belief and halted inspections.
Conclusion & Means Ahead
- A peaceable nuclear answer requires credible diplomacy, not simply power.
- Iran could push tougher for nuclear weapons as deterrence, even when regime adjustments.
- The U.S. should mix coercion with reassurance if it needs future offers to work.
CLIMATE CHANGE, COASTAL DISPLACEMENT, AND DEMOCRATIC CHALLENGES
TOPIC: (GS3) ENVIRONMENT: THE HINDU
Rising sea ranges, excessive climate, and unregulated growth are forcing coastal communities in India emigrate, revealing severe gaps in authorized safety, rehabilitation, and environmental justice.
Affect of Local weather Change on Coastal India
- Sea-level rise, saltwater intrusion, and coastal erosion are displacing conventional communities.
- States like Odisha, Karnataka, Tamil Nadu, Gujarat, and Kerala are witnessing large-scale climate-induced migration.
- Communities counting on fishing, farming, and coastal assets are the worst affected.
Unregulated Growth and Environmental Loss
- Initiatives like ports, aquaculture, and tourism beneath schemes equivalent to Sagarmala are degrading ecosystems.
- Mangroves, dunes, and wetlands—pure protectors—are being destroyed.
- Environmental clearances typically ignore local weather vulnerability and cumulative danger.
Migration and Labour Exploitation
- Displaced folks transfer to city areas like Chennai, Bhubaneswar, and Mumbai.
- Many find yourself in casual jobs as development, brick kiln, or home staff.
- Points embrace:
- Debt bondage as a result of survival-based wage advances.
- Lack of authorized safety beneath labour legal guidelines like BOCW Act, 1996.
- Girls face abuse, underpayment, and trafficking dangers.
Authorized and Coverage Gaps
- No devoted regulation for climate-induced migration in India.
- Current legal guidelines just like the Catastrophe Administration Act, 2005, EPA 1986, and CRZ Notification 2019 give attention to atmosphere however not displacement.
- CRZ 2019 has diluted protections, permitting industrial use in fragile zones.
- NAPCC and State Plans point out vulnerability however lack clear rehabilitation mechanisms.
Want for Rights-Primarily based Framework
- Combine local weather migrants into city planning and labour insurance policies.
- Amend labour codes to incorporate protections for displaced staff.
- Restore give attention to community-led coastal safety over industrial growth.
- Align insurance policies with SDG Goal 8.7 on eliminating pressured labour and making certain first rate work.
Grassroots Resistance and Constitutional Values
- Actions like Save Satabhaya (Odisha), Ennore protests (Tamil Nadu), and Pattuvam Mangrove Safety (Kerala) present sturdy group resistance.
- Protesters typically face surveillance and intimidation, weakening democratic rights.
- Upholding Article 21 and environmental justice is significant in local weather responses.
CRZ RULES (COASTAL REGULATION ZONE RULES)
CRZ (Coastal Regulation Zone) Guidelines are laws issued by the Ministry of Setting, Forest and Local weather Change (MoEFCC) beneath the Setting Safety Act, 1986, to handle and defend India’s coastal atmosphere.
They purpose to regulate actions alongside India’s 7,500 km shoreline to: Preserve ecologically delicate coastal areas, Forestall unregulated growth, NSteadiness environmental safety and financial exercise.
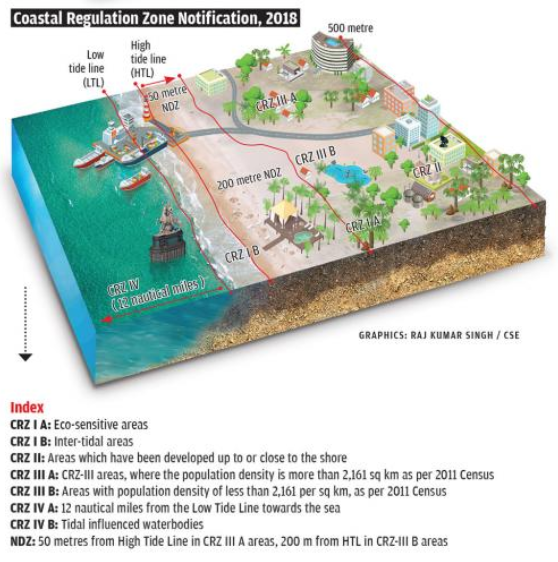
CRZ areas are categorized into 4 classes:
- CRZ-I: Ecologically delicate areas like mangroves, coral reefs, nationwide parks, and many others. No development allowed, apart from important providers.
- CRZ-II: City and developed areas near the shoreline. Regulated development allowed, as per city planning norms.
- CRZ-III: Rural and comparatively undeveloped areas, not falling beneath CRZ-I or II. Restricted development permitted past 200 metres from Excessive Tide Line (HTL).
- CRZ-IV: Water space from Low Tide Line to 12 nautical miles into the ocean and tidal-influenced water our bodies. Regulates fishing and discharges.
Conclusion:
India should deal with local weather displacement as a central a part of its local weather adaptation technique. Defending susceptible communities isn’t just about atmosphere—it’s a constitutional and democratic accountability.
NIPAH CASE IN PALAKKAD
TOPIC: (GS3) SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY: THE HINDU
A girl from Palakkad, Kerala, examined optimistic for Nipah virus and is in essential situation. The federal government has began strict containment and surveillance efforts to cease the virus from spreading.
In regards to the Nipah Outbreak in Palakkad
- That is the first Nipah case in Palakkad district.
- 173 folks recognized as contacts:
- 12 people are in isolation; 5 examined damaging, and 4 extra samples are beneath testing.
Containment and Monitoring
- A 3 km space across the affected person’s home declared a containment zone. Authorities are specializing in individuals who had contact with the affected person after July 1.
- Previous deaths as a result of mind points are additionally being re-examined.
- Animal deaths close by are beneath shut watch.
Authorities Measures and Public Response
- Kerala Well being Minister warned towards spreading misinformation.
- State is providing social and psychological assist to quarantined people.
- Kerala had earlier managed Nipah in 2018 and 2023 with comparatively low fatality charges.
WHAT IS NIPAH VIRUS?
Nipah virus (NiV) is a zoonotic virus, which means it spreads from animals to people. It belongs to the Paramyxoviridae household and the Henipavirus genus.
Pure Host and Transmission
- The pure host of Nipah is the fruit bat, particularly the Pteropus species (additionally known as flying foxes).
- The virus can unfold to people by means of:
- Direct contact with contaminated bats, pigs, or their physique fluids.
- Consuming fruits contaminated by bat saliva or urine.
- Human-to-human transmission through shut contact with contaminated folks.
Signs of Nipah An infection
- Preliminary signs: Fever, headache, muscle ache, vomiting, and sore throat.
- It could possibly shortly worsen to:
- Extreme respiratory points
- Encephalitis (swelling of the mind), which might result in coma or dying.
Analysis and Remedy
- Recognized by means of lab assessments like RT-PCR (for virus detection) and ELISA (for antibodies).
- There may be no particular remedy or vaccine at present.
- Sufferers are given supportive care, like hydration, oxygen, and managing signs.
- Monoclonal antibodies are being examined as experimental remedies.
STUDYING IN MOTHER TONGUE INSTILS STRONG VALUES: CJI
TOPIC: (GS2) INDIAN POLITY: THE HINDU
Chief Justice of India (CJI) not too long ago emphasised the significance of studying in a single’s mom tongue, calling it important for private progress, sturdy ethical values, and cultural connection.
Background of Language and Schooling in India
- India is dwelling to over 1,300 mom tongues and 122 main languages.
- Historically, gurukuls and madrasas used Sanskrit, Pali, Persian, or native dialects.
- British colonial insurance policies launched English-based training, making a linguistic divide.
Current Authorities Initiatives
- NEP 2020 and Nationwide Curriculum Framework 2023 advocate educating within the mom tongue or dwelling language at the least as much as Grade 5, ideally until Grade 8.
- Supported by:
- Proper to Schooling Act (2009): Promotes native language use wherever attainable.
- NIPUN Bharat, Vidya Pravesh, NISHTHA FLN: Promote foundational studying in native languages.
- CBSE language mapping contains 52 Indian languages, even tribal ones like Bhutia and Sherpa.
Advantages of Educating in Mom Tongue
- Higher Understanding: Youngsters be taught sooner when taught in a well-recognized language.
- Boosts Confidence: Will increase cultural pleasure and sense of identification.
- Larger Efficiency: UNICEF & UNESCO research present higher studying and math outcomes in early grades.
- Lowers Dropouts: Encourages college participation and reduces early exits.
Challenges and Issues
- World Publicity: Lack of English could scale back entry to international training and jobs.
- Logistical Points: Too many languages in a single space make implementation robust.
- Lack of Sources: Few lecturers and textbooks in native languages.
- Switching Language Later: Transitioning to English in later lessons turns into arduous.
Means Ahead
- Bilingual Mannequin: Begin with the mom tongue and slowly introduce English.
- Instructor Coaching: Practice educators in a number of languages.
- Balanced Strategy: Respect variety whereas following nationwide requirements.
INDIA RANKS 4TH AMONG THE WORLD’S MOST EQUAL SOCIETIES
TOPIC: (GS2) INTERNATIONAL RELATIONS: PIB
The World Financial institution has ranked India because the 4th most equal nation globally based mostly on its Gini Index rating of 25.5, indicating low revenue inequality.
What’s the Gini Index?
- It measures how evenly revenue or consumption is unfold amongst folks in a rustic.
- The rating ranges from 0 to 100: 0 means good equality.100 means full inequality.
- A decrease Gini Index means higher revenue equality.
India’s World Rating and Comparability
- India ranks 4th globally, behind Slovak Republic, Slovenia, and Belarus.
- India’s Gini rating: 25.5 – thought-about “reasonably low inequality” (rating between 25–30).
- India fared a lot better than: China: 35.7, USA: 41.8, 167 different nations within the World Financial institution dataset.
Poverty Discount in India
- Excessive poverty fell to 2.3% in 2022–23.
- 171 million folks moved out of utmost poverty from 2011 to 2023.
- Exhibits a powerful hyperlink between poverty discount and revenue equality.
Key Authorities Schemes That Promoted Equality
- PM Jan Dhan Yojana: Over 55.69 crore financial institution accounts assist direct switch of advantages.
- Aadhaar and DBT: Ensures correct, leak-proof supply of subsidies and pensions.
- Ayushman Bharat: Provides ₹5 lakh well being protection per household. Expanded to aged (70+) beneath Ayushman Vay Vandana Yojana. Digital Mission: Linked 79 crore well being accounts.
- Stand-Up India: Offers loans for SC/ST and girls entrepreneurs (₹10 lakh–₹1 crore).
- PMGKAY: Free ration to the poor throughout and after COVID-19.
- PM Vishwakarma Yojana: Helps conventional artisans with loans, digital instruments, and coaching.
Conclusion
India’s Gini Index rating of 25.5 is an indication of great progress towards equality. With the assistance of welfare schemes and know-how, India has mixed financial progress with social equity.
INVISIBLE HAND IN INDIA’S FOREIGN TRADE
TOPIC: (GS3) ECONOMY: THE HINDU
The Financial Survey 2024–25 highlights a significant shift in India’s international commerce, the place invisibles like providers exports and remittances now play a much bigger function than bodily items.
India’s Rising Service Sector
- The providers sector contains areas like IT, finance, tourism, healthcare, training, communication, and logistics.
- In FY25, it contributed about 55% of India’s GVA, up from 50.6% in FY14.
- It constantly grows at over 6% yearly, reaching 8.3% post-pandemic.
India’s World Place in Providers
- India is now the seventh largest exporter of providers with a 4.3% international share.
- In FY25 (Apr–Nov), service exports grew by 12.8%, up from 5.7% in FY24.
- Laptop and enterprise providers kind about 70% of complete providers exports.
- Remittances and IT providers assist keep a steady present account deficit.
Strengths and Alternatives
- India has a powerful expert workforce, particularly in knowledge-based providers.
- Authorities missions like Digital India, Sensible Cities, and Clear India assist service progress.
- The sector has the potential to create a multi-trillion-dollar financial alternative globally.
Key Challenges
- Digital and bodily infrastructure is weaker in rural and semi-urban areas.
- There’s a lack of expert staff for high-value service jobs.
- Advanced laws and restricted market entry hinder exports.
- Weak to international financial slowdowns.
Authorities Measures
- Champion Sector Motion Plan targets 12 focus areas like tourism, aiming for $50.9 billion income by 2028.
- Jan Dhan Yojana promotes monetary inclusion with 47 crore+ accounts.
- FDI limits elevated in insurance coverage to spice up funding.
- Assist for training, healthcare, and manufacturing by means of packages like Ayushman Bharat and PLI schemes.
Conclusion
India’s service sector is essential for job creation, exports, and progress. Give attention to higher infrastructure, talent growth, regulatory reforms, and international outreach can assist India develop into a international service hub—the true “workplace of the world.”
INDIA’S FIRST GLOBALLY RECOGNISED EQUINE DISEASE-FREE COMPARTMENT (EDFC)
TOPIC: (GS3) SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY: THE HINDU
India has launched its first Equine Illness-Free Compartment (EDFC) on the RVC Centre & Faculty in Meerut, Uttar Pradesh, which has now been recognised by the World Organisation for Animal Well being (WOAH).
About Equine Illness-Free Compartment (EDFC)
- It’s a designated space the place horses and different equines are saved beneath strict well being protocols to make sure they’re free from contagious illnesses.
- This enables secure worldwide motion of equines for occasions, breeding, or commerce.
- The ability is established on the Remount Veterinary Corps (RVC) Centre & Faculty, beneath the Indian Military, in Meerut Cantonment.
World Recognition
- The EDFC has been formally permitted by WOAH (World Organisation for Animal Well being).
- This makes India eligible to export disease-free equines to different nations for the primary time with international requirements.
- It boosts India’s status in veterinary well being administration and opens up new avenues in equine sports activities and commerce.
What are Equine Illnesses?
- These have an effect on horses, ponies, donkeys, and their hybrids.
- They are often attributable to viruses, micro organism, parasites, or different sources.
- Some are infectious and unfold shortly, affecting animal well being and commerce.
- Key examples embrace: Equine Influenza, Equine Infectious Anemia, Piroplasmosis, Surra, Glanders
India’s Equine Well being Standing
- India has been freed from African Horse Illness since 2014, a significant equine viral illness.
- The organising of this compartment reveals India’s readiness to adjust to worldwide well being requirements.
Significance of EDFC
- Promotes secure commerce and international competitiveness of Indian equines.
- Encourages participation in worldwide horse occasions and equestrian sports activities.
- Improves biosecurity, animal well being infrastructure, and helps rural livelihoods tied to equine rearing.
The publish Every day Present Affairs 08-July-2025 first appeared on Ekam IAS Academy.