JUDICIAL SENSITIVITY TO SENTIMENTS: A SIGN OF REGRESSION
TOPIC: (GS2) INDIAN POLITY: THE HINDU
Lately, courts in India have more and more been seen demanding apologies for speech that offends, focusing extra on sentiments than on upholding free speech. This pattern is being criticized for undermining Article 19(1)(a) of the Structure, which safeguards the basic proper to free speech.
Courts Managing Speech, Not Defending It
- Courts more and more ask people to apologize for offensive however lawful speech.
- They give attention to how one thing is alleged quite than why the best to say it’s essential.
- This weakens the citizen’s energy to query authority.
Outrage Over Substance
- Instance: A younger man criticized the Prime Minister on social media however the court docket refused to dismiss the FIR, prioritizing nationwide sentiments over free speech.
- Courts typically equate emotional harm with authorized hurt, which isn’t the take a look at underneath Article 19(2).
Recognition Check for Speech
- Courts advise apologies to the general public for speech that’s lawful however controversial.
- Instance: Kamal Haasan’s remarks about Kannada led to a suggestion for an apology quite than a authorized evaluation.
- This empowers mobs to litigate and chill free speech.
The Chilling Impact
- Courts deal with speech that offends establishments as defamation with out rigorous scrutiny.
- Even humorous or vital remarks can result in FIRs underneath harsh legal guidelines like sedition, deterring open dialogue.
- This course of itself punishes the speaker and discourages dissent.
Options Advised
- Courts ought to uphold free speech robustly, specializing in whether or not the speech incites violence, not whether or not it offends.
- Apologies needs to be voluntary, not a judicial prescription.
- Legal guidelines like sedition and broad “public order” clauses needs to be interpreted narrowly to guard liberty.
- Judges should be protectors of constitutional rights, not guardians of sentiments.
LANDMARK SUPREME COURT JUDGMENTS ON FREEDOM OF SPEECH
Maneka Gandhi vs Union of India (1978)
- Key Level: This case expanded the understanding of basic rights, together with the best to freedom of speech and expression underneath Article 19(1)(a).
- Judgment: The Supreme Courtroom dominated that any restriction on basic rights should be “cheap” and comply with the “process established by regulation.”
- It emphasised that freedom of speech is crucial for democracy and any regulation curbing it should be truthful, simply, and never arbitrary.
- This case additionally established that the best to freedom shouldn’t be restricted to the act itself however contains the best to know the explanations for any restriction.
Shreya Singhal vs Union of India (2015)
- Key Level: This case handled freedom of speech within the context of on-line content material and the Web.
- Judgment: The Supreme Courtroom struck down Part 66A of the IT Act, which was used to arrest individuals for posting “offensive” content material on-line.
- The Courtroom held that the regulation was imprecise and violated the basic proper to free speech as a result of it imposed unreasonable restrictions.
The ruling strengthened that freedom of expression applies to digital communication and shouldn’t be curbed until it threatens sovereignty, safety, or public order.
Conclusion
India’s democracy is dependent upon defending dissent and free speech, even when it’s offensive. Judicial sensitivity to sentiments weakens democratic values and emboldens those that need to stifle vital voices.
PRELIMS PRACTICE QUERSTIUON:
Which of the next restrictions are allowed underneath Article 19(2) of the Indian Structure regarding the best to freedom of speech and expression?
- Safety of the State
- Pleasant relations with international states
- Safety of pursuits of minorities
- Imposition of emergency
Choose the right reply utilizing the code under:
- 1 and a couple of solely
- 1, 2 and three solely
- 2, 3 and 4 solely
- 1, 2, 3 and 4
Reply: (b)
DECLINING POVERTY IN INDIA
TOPIC: (GS2) SOCIAL JUSTICE: THE HINDU
Latest information from the World Financial institution exhibits a pointy decline in excessive poverty in India, dropping from 27.1% in 2011-12 to five.3% in 2022-23. This vital change highlights progress but additionally raises questions on information assortment and its use for policymaking.
Developments in Poverty Discount
- Excessive poverty in India fell drastically from 27.1% in 2011-12 to 5.3% in 2022-23, in line with the newest World Financial institution figures.
- The poverty threshold utilized by the World Financial institution was raised to $3 per day from the earlier $2.15, making this decline much more exceptional.
- In absolute phrases, the variety of individuals dwelling in excessive poverty dropped from about 344 million to 75 million over this era.
- Even with a better poverty line of $4.2 per day (for lower-middle-income international locations), poverty decreased from 57.7% to 23.9% between 2011-12 and 2022-23.
- This decline seems to be persevering with past 2023.
Knowledge Challenges and Authorities Efforts
- The accuracy of poverty information has been debated resulting from lacking official information for 2017-18 over “information high quality points.”
- To deal with this, the federal government performed new family consumption expenditure surveys in 2022-23 and 2023-24.
- These new surveys assist present up to date and dependable insights into poverty tendencies over the past decade.
Multidimensional Poverty and Inequality
- NITI Aayog reported a fall in multidimensional poverty — which incorporates well being, training, and dwelling requirements — from 55.3% in 2005-06 to 15% in 2019-21.
- The World Financial institution additionally famous a decline in inequality in India between 2011 and 2022, utilizing measures just like the Gini and Theil indices.
- Nevertheless, inequality measured by consumption information tends to indicate decrease ranges than income-based inequality.
Coverage Implications
- Up to date poverty and inequality information are essential for policymakers to design better-targeted welfare and improvement applications.
- Dependable information helps in monitoring progress and making knowledgeable selections to additional cut back poverty and enhance dwelling requirements.
Conclusion:
The numerous decline in poverty in India displays constructive financial and social progress, however dependable information stays essential for efficient policymaking. Continued efforts are wanted to maintain this momentum and handle remaining challenges.
CONSULTATIVE REGULATION-MAKING NEEDS FURTHER REFORMS
TOPIC: (GS3) ECONOMY: THE HINDU
The Reserve Financial institution of India (RBI) and the Securities and Alternate Board of India (SEBI) just lately launched new frameworks to make the method of creating rules extra open and participatory.
Optimistic Developments
- RBI now requires “affect evaluation” earlier than making new rules or amending current ones.
- SEBI should clarify the aim of proposed rules and each regulators will now invite public suggestions for 21 days.
- They may even often evaluate their rules to verify if they’re nonetheless related.
Areas for Additional Enchancment
Want for Financial Rationale
- Rules ought to clearly clarify the financial purpose for his or her existence.
- They need to establish particular market failures or points they purpose to deal with.
- Worldwide practices (e.g., US and EU) require a cost-benefit evaluation and the analysis of options earlier than imposing new rules.
- Presently, RBI and SEBI point out broad targets however don’t clearly hyperlink proposed guidelines to financial issues.
Strengthening Accountability
- Previous information present RBI and SEBI not often sought public feedback on rules, with RBI doing so on simply 2.4% of circulars in a single 12 months.
- To enhance accountability, regulators ought to:
- Report what number of rules have been open for public suggestions.
- Share what number of options have been accepted or rejected and why.
- Disclose how public enter influenced the ultimate guidelines.
- SEBI typically excludes summaries of public feedback, citing confidentiality, which undermines belief.
Periodic Critiques
- RBI and SEBI ought to set clear timelines for reviewing rules to see if they’re working as supposed.
- The Worldwide Monetary Companies Centres Authority (IFSCA) already requires a evaluate each three years, which is an efficient instance.
Broader Reforms Wanted
- Restricted capability in regulatory our bodies makes thorough affect assessments troublesome.
- Piecemeal reforms might not be sufficient; Parliament might move a regulation just like the US Administrative Process Act to set customary procedures for making rules, together with obligatory public session and affect evaluation.
Conclusion
RBI and SEBI have taken necessary steps to enhance regulation-making. Nevertheless, extra reforms are wanted to make sure these processes are clear, accountable, and based mostly on clear financial logic. India ought to study from worldwide greatest practices to construct a stronger regulatory framework.
DEFENCE PRODUCTION IN INDIA
TOPIC: (GS3) ECONOMY: THE HINDU
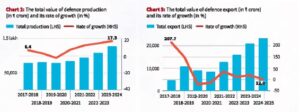
India’s defence manufacturing reached a report excessive in FY24, crossing ₹1.3 lakh crore and exhibiting sturdy progress. Personal corporations and MSMEs have contributed considerably to this progress, whereas defence exports have additionally surged.
Defence Manufacturing Developments
- India’s defence manufacturing touched ₹1.3 lakh crore in FY24, a 17% rise from the earlier 12 months.
- That is the second consecutive 12 months manufacturing has crossed ₹1 lakh crore, highlighting constant progress.
- Progress charges have been in double digits since FY22, recovering from a contraction of -2.5% in FY20.
Defence Exports on the Rise
- India’s defence exports exceeded ₹20,000 crore in FY23 and FY24, double the degrees earlier than FY20.
- Key export gadgets embody small arms, protecting tools, and artillery.
- The federal government has set an formidable export goal of ₹30,000 crore for FY25.
- Exports confirmed regular progress lately regardless of some fluctuations within the price of progress (Chart 3).
Position of Personal Firms
- Public sector corporations proceed to dominate, however non-public corporations’ share has grown from round 20% in FY17 to about 24% in FY25.
- Personal corporations additionally maintain a big share of defence exports resulting from simpler export clearances.
- This means a shift in direction of a extra balanced manufacturing ecosystem (Chart 4).
Contribution of MSMEs
- MSMEs have grow to be key gamers by supplying elements to defence producers.
- In FY25, procurement from MSMEs reached ₹13,000 crore, greater than double the 12 months’s goal.
- Beforehand, annual procurement from MSMEs was round ₹3,000 crore between FY18-FY20, however has grown considerably since (Chart 5).
Inventory Market Developments
- Defence shares noticed a pointy rise after Operation Sindoor.
- Week of the strike: Defence shares rose by 20.8%, in comparison with 3.1% rise in Nifty50.
- Subsequent week: Defence shares grew 5.4% whereas Nifty50 fell by 0.5% (Chart 1).
- This surge highlights elevated investor confidence within the defence sector throughout geopolitical tensions.
Challenges
- Regardless of progress, defence’s share in general authorities spending has declined.
- India nonetheless spends a better proportion of GDP on its army in comparison with many rising markets.
Conclusion
India’s defence manufacturing and export progress alerts a constructive shift in direction of self-reliance. With rising contributions from non-public corporations and MSMEs, India is constructing a stronger home defence trade, although challenges stay.
THE SIGNIFICANCE OF THE CENSUS
TOPIC: (GS2) INDIAN POLITY: THE HINDU
The Union Dwelling Ministry introduced that the subsequent Census can be held in two phases with March 1, 2027, because the reference date. Will probably be India’s first Census after an extended delay as a result of COVID-19 pandemic and contains plans to gather caste information.
When was the primary Census performed?
- The primary synchronous Census in India started in 1881 throughout British rule.
- W. C. Plowden was the primary Census Commissioner.
- Since then, it has been performed each 10 years, apart from the delay in 2021 resulting from COVID-19.
How is the Census performed?
- Union Checklist Topic: The Census is listed underneath the Union Checklist, that means it’s the duty of the Central authorities.
- Key Legislation: The Census Act, 1948, regulates the method.
- Two Phases:
- Part 1: Home Itemizing — Collects information on housing circumstances and family property over 5-6 months.
- Part 2: Inhabitants Enumeration — Captures particulars like identify, age, intercourse, faith, caste (SC/ST), literacy, and occupation.
- The info is compiled and revealed in provisional and remaining experiences.
Why is caste being counted within the upcoming Census?
- Earlier, solely SC and ST classes have been recorded.
- As a result of calls for from numerous political events and social teams, the federal government determined to gather caste information for all Hindus.
- This may assist in formulating insurance policies for backward courses.
Why are southern and smaller States involved?
- States like these within the south and a few smaller states worry that population-based seat redistribution may cut back their political illustration.
- They fear about shedding Lok Sabha seats within the subsequent delimitation train after the 2027 Census.
- Many have requested for a freeze on the present variety of seats to keep away from shedding affect.
Significance of the Present Census
- First Census after 2026: Might affect the delimitation of seats in Parliament and State Assemblies.
- Girls’s Reservation: Knowledge could also be used to order one-third of seats for ladies.
- Coverage Planning: Important for social welfare, useful resource allocation, and governance selections.
Approach Ahead
- Caste information should be collected rigorously to make sure accuracy and reliability.
- States’ issues about illustration should be addressed with consensus earlier than implementing seat adjustments.
- Delimitation needs to be completed cautiously, making certain that no state is unfairly handled.
- Girls’s reservation needs to be applied based mostly on dependable information from this Census.
INDIA PLANNING TO LOCALISE EV MANUFACTURING
TOPIC: (GS3) ECONOMY: THE HINDU
The Ministry of Heavy Industries (MHI) just lately notified the rules for the Scheme to Promote Manufacturing of Electrical Passenger Automobiles in India. This scheme goals to spice up home EV manufacturing and cut back dependence on imports.
Highlights of the Scheme
- Lowered Customs Obligation: Presently, totally constructed electrical automobiles entice 70-100% customs responsibility. Below the brand new scheme, this responsibility can be decreased to fifteen% for imported EVs priced at $35,000 or extra.
- Funding Requirement: To get this profit, corporations should make investments not less than ₹4,150 crore in India inside three years. They have to additionally develop infrastructure and services to assist home manufacturing.
- Localization Targets: At the least 25% of producing should be native inside three years. This determine ought to rise to 50% inside 5 years.
- Import Cap: A most of 8,000 automobiles will be imported yearly on the decreased responsibility price. The utmost customs responsibility profit allowed underneath the scheme is ₹6,484 crore.
Potential Advantages
- Can encourage world EV gamers to arrange crops in India, creating jobs.
- Goals to strengthen native provide chains and part manufacturing.
- Helps India’s targets of lowering carbon emissions and selling clear vitality.
Challenges and Considerations
- Expertise Switch: Specialists warn that with out correct expertise sharing, native gamers could not profit totally. International locations are normally hesitant to share superior expertise, so India should plan accordingly.
- Give attention to 4-Wheelers: The coverage emphasizes passenger automobiles, however two-wheelers and three-wheelers dominate EV gross sales. Majority of Indians depend on public transport, which additionally wants consideration.
- Affect on Native Business: Firms like Tata Motors have opposed decreased import duties, fearing hurt to native gamers. Native producers need extra assist to construct capability earlier than competing with world manufacturers.
Encourage e-mobility
- FAME India Part II: Provides subsidies for electrical two-wheelers, three-wheelers, and buses, together with tax incentives on automobiles and elements to cut back prices and improve adoption.
- Lowered GST on EVs: Items and Companies Tax (GST) on EVs has been decreased from 12% to five%, encouraging patrons and producers to modify to electrical.
- Earnings Tax Deduction on EV Mortgage Curiosity: Below Part 80EEB of the Earnings Tax Act, people can declare a deduction of as much as ₹1.5 lakh on curiosity paid on loans for purchasing EVs.
- PLI Scheme for Superior Chemistry Cell Batteries: Supplies monetary incentives to producers investing in home battery manufacturing, decreasing prices and boosting native EV provide chains.
Approach Ahead
- India ought to give attention to constructing abilities, R&D, and expertise switch.
- Insurance policies should steadiness attracting international funding and supporting native corporations.
- The scheme should additionally embody plans for public transport and smaller EV segments.
Conclusion:
India’s push to localize EV manufacturing can enhance the economic system, generate jobs, and cut back carbon emissions, however success is dependent upon balanced insurance policies that foster expertise switch and assist all EV segments. Inclusive progress in e-mobility requires consideration to public transport and smaller automobiles alongside passenger automobiles.
UPSC MAINS PRACTICE QUESTION:
“Study the challenges and alternatives in selling home electrical automobile manufacturing in India. How can authorities insurance policies guarantee balanced progress of the EV sector whereas defending native industries?”
INDIA’S WIND SECTOR
TOPIC: (GS3) ECONOMY: THE HINDU
India goals to achieve 500 GW of non-fossil vitality by 2030, together with over 100 GW from wind energy. Considerations have emerged concerning the sector’s cybersecurity, expertise switch, and native innovation.
India’s Wind Vitality (2025)
- Put in Capability: As of FY 2024, India’s wind vitality capability stood at 16 GW, powering progress within the sector
- Share in Renewable Vitality Combine: Complete renewable vitality capability reached 4 GW, with wind making up about 23% of that blend (10.5% of renewable complete) .
- Non-fossil capability (together with renewables + nuclear & massive hydro) accounts for 8–47% of India’s 456.7 GW complete energy capability
- Total, Energy Combine: Complete put in capability is 7 GW, with 209.4 GW (≈47%) from renewables. Wind accounts for roughly 10.5% of the renewable section, translating to about 11% of complete energy capability .
- High 3 Wind-Producing States: Gujarat: ~12,474 MW, Tamil Nadu: ~11,409 MW, Karnataka: ~6,731 MW
Challenges in India’s Wind Sector
Cybersecurity Threats
- Renewable vitality networks depend on SCADA methods for operations.
- A cyberattack on these methods might disable wind farms in seconds.
- Stronger digital safety measures are solely now being launched.
Want for Localisation and Innovation
- Proposed insurance policies require wind turbine information to be saved inside India.
- International corporations will not have distant entry to Indian wind farms.
- OEMs (Authentic Gear Producers) should arrange R&D facilities in India to foster native innovation.
- India ought to purpose to design generators for its personal local weather and grid circumstances, not simply import expertise.
Local weather Adaptability
- India’s excessive circumstances (excessive temperatures, coastal air, monsoons) problem imported turbine designs.
- There isn’t a obligatory in-country testing to make sure generators can deal with India’s climate.
- With out this, India dangers utilizing generators that fail in harsh circumstances.
Software program Safety Considerations
- Wind generators use software-driven elements like energy converters and firmware.
- These methods will be weak to hidden software program bugs or backdoors.
- Obligatory safety audits are wanted, particularly for tools from international locations with geopolitical tensions.
Coverage Suggestions
- Implement sturdy rules for in-country R&D and prototype testing.
- Mandate local weather resilience testing for all wind generators earlier than approval.
- Embody cybersecurity necessities, like audits of software program and {hardware}, in vendor certifications.
- Strengthen the regulatory framework to make pointers obligatory, not non-compulsory.

Conclusion
India’s wind sector should give attention to innovation, safety, and localised options. Insurance policies should guarantee generators usually are not simply made in India however actually designed for Indian circumstances.
INDIA-MONGOLIA JOINT MILITARY EXERCISE
TOPIC: (GS2) INTERNATIONAL RELATIONS: THE HINDU
The seventeenth version of the joint army train ‘Nomadic Elephant’ is at the moment being held from Could 31 to June 13, 2025, in Mongolia. The train goals to spice up cooperation and interoperability between Indian and Mongolian forces.

Key Options of the Train
- Focus Areas: Non-conventional operations in semi-urban and mountainous areas underneath UN mandate. Sharing greatest practices in counter-terrorism and precision capturing.
- Coaching Targets: Improve the operational skills of each armies. Construct coordination and understanding in advanced terrains.
- UN Peacekeeping: Contains simulations of UN peacekeeping missions to enhance cooperation in real-world eventualities.
- Cultural Alternate: Emphasizes cultural understanding and friendship between the 2 forces.
Significance
- Strengthens defence ties between India and Mongolia.
- Prepares each international locations to cope with fashionable safety challenges.
The submit Each day Present Affairs 09-June-2025 first appeared on Ekam IAS Academy.